Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation (pain and swelling )of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body’s tissues are mistakenly attacked by their own immune system. Patients with autoimmune diseases have antibodies and immune cells in their blood that target their own body tissues, where they can be associated with inflammation. Inflammation attacks the joint lining called synovium of the causing inflammatory arthritis is characteristic features of rheumatoid arthritis, the disease can also cause inflammation and injury in other organs in the body. Because it can affect multiple other organs of the body, rheumatoid arthritis is referred to as a systemic illness and is sometimes called rheumatoid disease. Rheumatoid arthritis is a classic rheumatic disease. Rheumatoid arthritis that begins in people under 16 years of age is referred to as juvenile idiopathic arthritis or JIA (formerly juvenile rheumatoid arthritis or JRA).
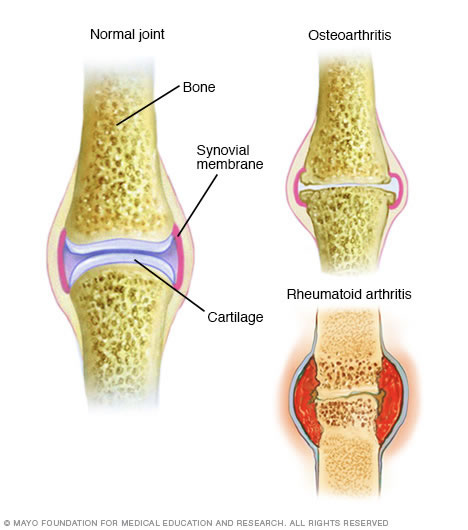
Unlike the wear-and-tear damage of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis affects the lining of your joints, causing a painful swelling that can eventually result in bone erosion and joint deformity.
The inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis is what can damage other parts of the body as well. While new types of medications have improved treatment options dramatically, severe rheumatoid arthritis can still cause physical disabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
It is not known what triggers the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Regardless of the exact trigger, the result is an immune system that is geared up to promote inflammation in the joints and occasionally other tissues of the body. Immune cells, called lymphocytes, are activated and chemical messengers (cytokines, such as tumornecrosis factor/TNF, interleukin-1/IL-1, and interleukin-6/IL-6) are expressed in the inflamed areas.
Environmental factors also seem to play some role in causing rheumatoid arthritis. For example, scientists have reported that smoking tobacco, exposure to silica mineral, and chronic periodontal disease all increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. There are theories about different gut bacteria (the microbiome of gut microbes that naturally inhabit the lining of the bowels) that might trigger the onset of rheumatoid arthritis in genetically susceptible individuals. No specific microbes have been identified as definite causes.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis may include:
- Tender, warm, swollen joints
- Joint stiffness that is usually worse in the mornings and after inactivity
- Fatigue, fever and weight loss
Early rheumatoid arthritis tends to affect your smaller joints first — particularly the joints that attach your fingers to your hands and your toes to your feet.
As the disease progresses, symptoms often spread to the wrists, knees, ankles, elbows, hips and shoulders. In most cases, symptoms occur in the same joints on both sides of your body.
About 40 percent of the people who have rheumatoid arthritis also experience signs and symptoms that don’t involve the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect many nonjoint structures, including:
- Skin
- Eyes
- Lungs
- Heart
- Kidneys
- Salivary glands
- Nerve tissue
- Bone marrow
- Blood vessels
Rheumatoid arthritis signs and symptoms may vary in severity and may even come and go. Periods of increased disease activity, called flares, alternate with periods of relative remission — when the swelling and pain fade or disappear. Over time, rheumatoid arthritis can cause joints to deform and shift out of place.
Rheumatoid arthritis increases your risk of developing:
- Osteoporosis. Rheumatoid arthritis itself, along with some medications used for treating rheumatoid arthritis, can increase your risk of osteoporosis — a condition that weakens your bones and makes them more prone to fracture.
- Rheumatoid nodules. These firm bumps of tissue most commonly form around pressure points, such as the elbows. However, these nodules can form anywhere in the body, including the lungs.
- Dry eyes and mouth. People who have rheumatoid arthritis are much more likely to experience Sjogren’s syndrome, a disorder that decreases the amount of moisture in your eyes and mouth.
- Infections. The disease itself and many of the medications used to combat rheumatoid arthritis can impair the immune system, leading to increased infections.
- Abnormal body composition. The proportion of fat compared to lean mass is often higher in people who have rheumatoid arthritis, even in people who have a normal body mass index (BMI).
- Carpal tunnel syndrome. If rheumatoid arthritis affects your wrists, the inflammation can compress the nerve that serves most of your hand and fingers.
- Heart problems. Rheumatoid arthritis can increase your risk of hardened and blocked arteries, as well as inflammation of the sac that encloses your heart.
- Lung disease. People with rheumatoid arthritis have an increased risk of inflammation and scarring of the lung tissues, which can lead to progressive shortness of breath.
- Lymphoma. Rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of lymphoma, a group of blood cancers that develop in the lymph system.
- Sjogren’s Syndrome
- Inflammation of the glands of the eyes and mouth can cause dryness of these areas and is referred to as Sjögren’s syndrome. Dryness of the eyes can lead to corneal abrasion. Inflammation of the white parts of the eyes (the sclerae) is referred to as scleritis and can be very dangerous to the eye.
- Anemia : Rheumatoid disease can reduce the number of red blood cells (anemia) and white blood cells. Decreased
- Felty’s Syndrome: white cells can be associated with an enlarged spleen (referred to as Felty’s syndrome) and can increase the risk of infections. The risk of lymph gland cancer (lymphoma) is higher in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, especially in those with sustained active joint inflammation.
- Rheumatoid Nodules : Firm lumps or firm bumps under the skin (subcutaneous nodules called rheumatoid nodules) can occur around the elbows and fingers where there is frequent pressure. Even though these nodules usually do not cause symptoms, occasionally they can become infected.
- Carpal tunnel Syndrome : Nerves can become pinched in the wrists to cause carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Vasculitis : A rare, serious complication, usually with longstanding rheumatoid disease, is blood vessel inflammation (vasculitis). Vasculitis can impair blood supply to tissues and lead to tissue death (necrosis). This is most often initially visible as tiny black areas around the nail beds or as leg ulcers.
During the physical exam, your doctor will check your joints for swelling, redness and warmth. He or she may also check your reflexes and muscle strength.
What is the treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis ?
Treatment oThere is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis. But recent discoveries indicate that remission of symptoms is more likely when treatment begins early with strong medications known as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
- NSAIDs. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Over-the-counter NSAIDs include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB) and naproxen sodium (Aleve). Stronger NSAIDs are available by prescription. Side effects may include ringing in your ears, stomach irritation, heart problems, and liver and kidney damage.
- Steroids. Corticosteroid medications, such as prednisone, reduce inflammation and pain and slow joint damage. Side effects may include thinning of bones, weight gain and diabetes. Doctors often prescribe a corticosteroid to relieve acute symptoms, with the goal of gradually tapering off the medication.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). These drugs can slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and save the joints and other tissues from permanent damage. Common DMARDs include methotrexate (Trexall, Otrexup, Rasuvo), leflunomide (Arava), hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) and sulfasalazine (Azulfidine). Side effects vary but may include liver damage, bone marrow suppression and severe lung infections.
- Biologic agents. Also known as biologic response modifiers, this newer class of DMARDs includes abatacept (Orencia), adalimumab (Humira), anakinra (Kineret), certolizumab (Cimzia), etanercept (Enbrel), golimumab (Simponi), infliximab (Remicade), rituximab (Rituxan), tocilizumab (Actemra) and tofacitinib (Xeljanz).
These drugs can target parts of the immune system that trigger inflammation that causes joint and tissue damage. These types of drugs also increase the risk of infections.
Biologic DMARDs are usually most effective when paired with a nonbiologic DMARD, such as methotrexate.
Assistive devices can make it easier to avoid stressing your painful joints. For instance, a kitchen knife equipped with a saw handle helps protect your finger and wrist joints. Certain tools, such as buttonhooks, can make it easier to get dressed. Catalogs and medical supply stores are good places to look for ideas.
Rheumatoid arthritis surgery may involve one or more of the following procedures:

